The Rise of Blockchain Technology and Its Implications for the Future of Finance
Due to its success as an intermediary-free platform, blockchain has lately become a frequently used information system technology. There aren’t many exploratory studies available to show how the field is developing, despite the use of blockchain in several industries, such as finance, supply chains, healthcare, education, and energy consumption, which is increasingly enabling the development of Internet-enabled “distributed databases.” Investigating how blockchain technology is currently applied in the financial sector will help businesses achieve a competitive edge.
This systematic examination of the literature evaluates the content of the 50 most significant academic publications and professional industry reports produced between 2008 and 2022 to discover numerous potential characteristics of blockchain research in the financial sector. This study concentrated on the characteristics of blockchain technology, its function in finance, its benefits over rival technologies, the current condition of finance, and several problems that are impeding the widespread adoption of blockchain-based financial information systems. We have outlined three crucial areas that require study if blockchain technology is to become the “next-generation network” that revolutionizes the financial industry.
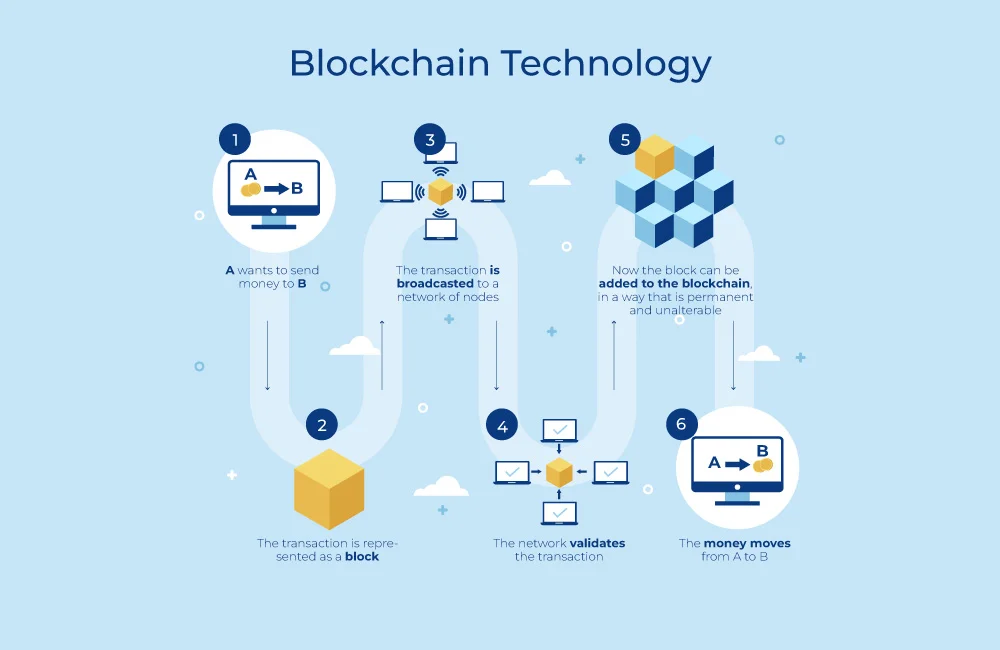
What Are Blockchains?
A blockchain is a digital, decentralized ledger that safeguards and prevents data manipulation. A unit, or “block,” is added to the chain whenever a transaction is made. Each additional transaction builds on the one before it, resulting in a safe log of all activities. Blockchain is dispersed throughout a computer network, removing the chance of a single point of failure. It is therefore a very stable and trustworthy system. To further ensure that it cannot be changed or destroyed, all data is encrypted. The blockchain is the ideal platform for storing sensitive data because no one entity has access to it. Although blockchain technology has many uses, it is most typically used in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
Just two of the numerous industries blockchain can revolutionize are supply chain management and the healthcare industry. Blockchain, for instance, might be used to build a decentralized, secure system for keeping track of medical records. Patients would have more control over their data as a result, and healthcare practitioners would find it simpler to exchange information and coordinate care. Similar to how supply chains may be streamlined, items could be tracked as they move around the globe using blockchain technology. This would lower the possibility of fraud while increasing transparency and accountability. As all parties will be using the same decentralized platform, voting methods are starting to integrate blockchain technology to help make elections more equal and fair.
Basics of blockchain technologies
Satoshi Nakamoto, an unidentified programmer or group of programmers, established the earliest and most basic blockchain technology in November 2008 as an electronic cash system, the distributed ledger powering Bitcoin transactions [24]. Given that this system consists of four essential parts, as illustrated in Fig. 2, a hash, a digital signature, a peer-to-peer network, and consensus processes, it was considered a paradigm change. The distributed digital ledger’s technology stores transactions as an immutable list of blocks that are spread across peers. There is no single point of failure because there is no requirement for a single server. Each block includes encrypted data and is linked to the one before it by a unique identity produced by the hashing technique.
Mining is the process of approving transactions and adding them to the blockchain; it requires highly tuned hardware and potent computational resources. Using a consensus mechanism, such as proof-of-stake (PoS), proof-of-work (PoW), proof-of-elapsed time (PoET), delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS), or practical byzantine fault tolerance (PBFT), many nodes (participants) can agree on whether a block is genuine. Blockchain technology offers security by encrypting each block’s transaction using the cryptographic hashing method Hash256. All of these elements improve the security, trust, privacy, and anonymity properties of the blockchain [25].
Revolution of blockchain technology
The first of these four stages of revolution for blockchain since 2008 is the introduction of cryptocurrencies, most notably Bitcoin (Fig. 3). Blockchain technology has gained popularity since the creation of Bitcoin. In the second era, financial transactions and smart contracts—automated computer programs that run automatically—were introduced in mortgages, loans, and other types of monetary bonds. By expanding the features of smart contracts, it has become more prevalent in the third era of the digital society. The fourth era is concerned with industrial decentralized ledger systems in a variety of sectors, including finance, governance, healthcare, supply chain management, and education [12]. From being a platform for digital currency to smart contracts to decentralized apps (DApp) with high-speed and extensible decentralized storage and decentralized communication to the infrastructure available for
What are the Benefits of Blockchain in Finance?
The Ethereum blockchain presents new banking and monetary products and usefulness, shared working models, more effective operations, lower prices, and more relaxed, inclusive, and secure corporate networks. It makes it possible to issue digital securities more quickly, more cheaply per unit, and with more customization. Thus, digital economic tools may be customized to meet the needs of investors, extending up new calls for investors, reducing issuer costs, and reducing counterparty risk.
The technology has developed for enterprise-grade applications during the past five years, displaying the following advantages:
Security: Its distributed consensus-based architecture minimizes single points of failure and decreases the need for ineffective monopolistic utilities, messaging system operators, and transfer agents as data intermediaries. Ethereum also makes it feasible to construct secure application code that is virtually impossible to hack or modify and is created to be tamper-proof against fraud and malevolent third parties.
Transparency: It uses mutualized standards, protocols, and common procedures and serves as a central repository of information for all network users.
Trust: Its transparent and irreversible ledger facilitates collaboration, data management, and agreement-making among various participants in a corporate network.
Programmability: It facilitates the formulation and execution of “smart contracts,” which are deterministic, tamper-proof programs that automate business logic and boost efficiency.
Privacy: It offers industry-leading technologies for precise data privacy across all software layers, enabling selective data sharing in corporate networks. While preserving confidentiality and privacy, this significantly improves transparency, trust, and effectiveness.
High-Performance: Its private and hybrid networks are designed to withstand a surge in network activity every so often and hundreds of transactions per second.
Scalability: It promotes interoperability across public and private chains, giving any enterprise solution the main net’s extensive reach, incredible durability, and great integrity.
By the end of 2030, banks will be able to save up to $27 billion on cross-border settlement transactions thanks to the deployment of blockchain technology, which will result in a more than 11% cost reduction. With over 10x cost benefits over established systems, Ethereum in particular has already proven disruptive economics. Financial institutions concur that distributed ledger technology will enable banks and other big financial institutions to save billions of dollars over the next 10 years.
Blockchain in the financial sector
Interest in blockchain has increased in the banking sector. The application of blockchain technology in financial operations such as international payments, identity verification, contracts, trade finance, insurance, auctions, and currency trading is increasingly pervasive. In Western nations including the USA, Australia, Canada, South Korea, Russia, and Israel, it has been pushed to develop blockchain-focused applications. [26] Cross-border payments, digital asset registration and administration, and cryptocurrencies and associated trading platforms are the three primary blockchain applications in finance that have been found (Fig. 4). Blockchain technologies, according to Deloitte [27], can be used to revolutionize the following financial processes: “intercompany transactions, procure-to-pay, order-to-cash, rebates, warranties, and trade financing.”
Systematic literature review methodology
Using the peer-reviewed literature that has been produced in the banking industry between 2008 and 2022, a systematic literature review was carried out in three phases (Fig. 5 depicts the specifics of the phases). Research on finance and studies on blockchain technology is included in our coverage. In the initial stage, we defined the research area’s scope while concentrating on blockchain technology in the finance industry. The study’s timeframe was derived from Satoshi Nakamoto’s 2008 publication of the first reference to the blockchain. Only peer-reviewed publications were chosen from the eight databases to ensure trustworthiness. Phase two was carried out using two basic methods. The “Abstract” portion of publications that were determined to be pertinent to the industry received the review’s initial focus.
The evaluation was then advanced to a more in-depth content study, where we needed to gather background information and comprehend the conceptual framework of blockchain in the finance industry. The review of the acquired data to ascertain its contributions to the subject was the first step in the final phase. Then, the findings were combined into a summary of both known and unidentified discoveries and disagreements. The study topics were then developed, and more research areas were found.
Findings and discussions
By contributing to and addressing difficulties pertinent to application design features, this review looked into the blockchain literature to provide beneficial research insights in the financial sector to assess its technical usefulness. Our investigation uncovered significant barriers to implementing ubiquitous smart applications as well as a crucial component of producing fresh conceptual understanding in the problem domain. Instead of concentrating on blockchain in the banking, finance, and FinTech categories in-depth, previous studies have attempted to study blockchain technology, its difficulties, and its applications in finance.
As far as we are aware, no reviews have either examined the proper theoretical foundation and empirical rigor or defined the topics that need to be included in a single research review. This is true even if past research on blockchain in finance revealed several areas for improvement. Our analysis, in contrast to other work, takes a broader view of blockchain in finance to support the claim that “The future of finance is blockchain” by describing the situation of the financial system now and how blockchain might transform it. We were aware of the disruptions brought on by technology and the difficulties associated with implementing blockchain. The business, technological, and social aspects of blockchain deployment were the three main areas of focus in our examination of the finance sector.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology’s development has caused a paradigm change in the banking sector. Its decentralized structure, increased security, and transparency are revolutionizing how money is transacted. Blockchain technology has several uses, including cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, and better. The future influence of this ground-breaking technology on banking will be mesmerizing to watch. Blockchain will continue to have an impact in ways that we don’t completely understand, thus we cannot ignore it.
Blockchain technology can completely transform the financial industry by improving digital transactions’ efficiency, accessibility, security, and transparency. This may result in lower operating expenses for companies, better cybersecurity safeguards, and smart contracts that allow for secure agreements between parties. We may anticipate more innovation and disruption in the finance sector as this technology develops. Companies should utilize blockchain’s many benefits as soon as feasible because the advantages it offers in the financial sector are obvious and considerable.


